++ 50 ++ gravitational force definition quizlet 147776-Gravitational force definition quizlet
It follows from the definition of gravitational field strength as the force per unit mass that the field strength at that point, g, is related to the mass of the Earth by the expression Gravitational field strength is a property of any point in a field It can be given aNewton's law of universal gravitation is usually stated as that every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centersQ Complete the following statement The farther away two planets are the _______ the gravitational force between them As a space ship of constant mass moves farther away from Earth, the strength of the gravitational interaction between the Earth and the space craft stays the same increases

Gravity Flashcards Quizlet
Gravitational force definition quizlet
Gravitational force definition quizlet-Synonyms for gravitational force include force of gravity, gravitation, gravitational attraction, gravity, downward pull, pull, attraction, downward force, downward pressure and force Find more similar words at wordhippocom!Weightlessness is the complete or nearcomplete absence of the sensation of weight This is also termed zeroG, although the more correct term is "zero Gforce" It occurs in the absence of any contact forces upon objects including the human body Weight is a measurement of the force on an object at rest in a relatively strong gravitational field These weightsensations originate from




Ib Physics Topic 6 2 And 10 2 Gravitation Diagram Quizlet
Start studying gravitational Force Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools8/10/10 · Gravitational force surrounds us It is what decides how much we weigh and how far a basketball will travel when thrown before it returns to the surface The gravitational force on · The gravitational force is a force that attracts any two objects with mass We call the gravitational force attractive because it always tries to pull masses together, it
Believed to be mediated by gravitonsInformation and translations of gravitational force in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web · Gravitation is one of the four fundamental forces of nature Of all four basic forces, gravitational force is the one that we are particularly familiar with The other forces are the weak nuclear force, electromagnetic force and strong nuclear force The weak and strong forces play a special role at the level of subatomic particles
· Gravitational Forces When you hold up a ball and let it go, you know it will fall to the ground You can also look up in the sky at night and see the moon pass overhead1 Only known planet to support life 2 71% of the earth is covered with water 3it takes 365 days for earth to revolve around the sun Earth 1 Known as the red planet iron rich soil 2has twoGravitational energy is the potential energy associated with gravitational force, as work is required to elevate objects against Earth's gravity The potential energy due to elevated positions is called gravitational potential energy, and is evidenced by water in




Astro Flashcards Quizlet




1 4 Gravity A Force Of Attraction Flashcards Quizlet
Wiktionary (500 / 1 vote) Rate this definition gravitational force (Noun) a very longrange, but relatively weak fundamental force of attraction that acts between all particles that have mass;Gravity is a force of attraction between objects due to their masses Gravity can change the motion of an object by changing the objects velocity Explain how mass effects gravity on matter All matter has mass and gravity is affected by the mass ofGravitational Force is an attraction force present between any two substances, objects or particles The force of gravity is not only the attraction force between the Earth and objects, but it exists between every substance or object in the universe The force of gravity is the reason that our earth revolves around the sun and the moon revolves




Gravitational Fields Flashcards Quizlet




Physics Gravity Gravitational Field Definitions Flashcards Quizlet
Gravity is a force which tries to pull two objects toward each other Anything which has mass also has a gravitational pull The more massive an object is, the stronger its gravitational pull is Earth's gravity is what keeps you on the ground and what causes objects to fallThe greater the mass the greater amount of force 1st Law The Law of Inertia An object at rest stays at rest, an object in motion stays in motion unless acted uponA gravitational force, in the simplest terms, is the attractive force between two separate bodies Gravity is related to mass the greater an object's mass, the greater the gravitational force it exerts on other objects It is one of the essential forces that account for the structure of




Unit 2 Vocabulary Words Flashcards Quizlet




Physics 1 Chapter 4 Forces And Laws Of Motion Flashcards Quizlet
· Gravitational acceleration (symbolized g) is an expression used in physics to indicate the intensity of a gravitational field It is expressed in meters per second squared (m/s 2)At the surface of the earth, 1 g is about 98 m/s 2 The use of the term acceleration in conjunction with gravity arises from Einstein's principle of equivalence, which was a cornerstone in theVideo shows what gravitational force means a very longrange, but relatively weak fundamental force of attraction that acts between all particles that haveIn theories of quantum gravity, the graviton is the hypothetical quantum of gravity, an elementary particle that mediates the force of gravity There is no complete quantum field theory of gravitons due to an outstanding mathematical problem with renormalization in general relativity In string theory, believed to be a consistent theory of quantum gravity, the graviton is a massless state of




Physics Chapter 4 Forces And The Laws Of Motion Flashcards Quizlet




Astronomy Test 3 Flashcards Quizlet
Joseph Priest, in Encyclopedia of Energy, 04 61 Gravitational Potential Energy The gravitational force on a box of mass m is mg, where g is the acceleration due to the gravitational force If the box is raised a height h, the work done by gravity is W=−mghThe change in potential energy of the box is then Δ U = − W conservative = mghThe positive sign means that theThat Jupiter's gravitational force is much stronger than Earth's gravitational force That Jupiter's and Earth's gravitational forces are equal Mass has no effect on the gravitational force between two objects s Question SURVEY 30 seconds Q · All these questions can be answered by understanding the concepts of gravitation The universal force of attraction, which is acting between objects, is known as the gravitational force What is Gravitational Force?
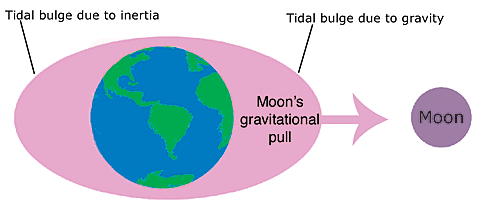



Gravity Inertia And The Two Bulges Tides And Water Levels Noaa S National Ocean Service Education




End Of The Year Review Part 6 Flashcards Quizlet
Definition of gravitational force in the Definitionsnet dictionary Meaning of gravitational force What does gravitational force mean?Define gravitational force gravitational force synonyms, gravitational force pronunciation, gravitational force translation, English dictionary definition of gravitational force n The weakest of the four fundamental forces of nature, being the attractive force that arises from gravitationalGravitational collapse is the contraction of an astronomical object due to the influence of its own gravity, which tends to draw matter inward toward the centre of gravity Gravitational collapse is a fundamental mechanism for structure formation in the universe Over time an initial, relatively smooth distribution of matter will collapse to form pockets of higher density, typically creating a




Gravity Flashcards Quizlet




Newton S Universal Law Of Gravitation Flashcards Quizlet
Everything u see near u is held by gravitational force and also u and your mobile in which u reading about gravity apple from tree comes down because of gravitation force, sky diving is possible because of gravity, surfing, boating, bike riding, wIn physics, gravity is the natural force that causes things to fall toward the earth The noun gravity can also mean seriousness or solemnityThe Gravitational force formula is given by \(F=\frac{Gm_{1}m_{2}}{r^{2}}\) Where, G is universal gravitational constant, m 1 and m 2 are mass of bodies r is the radius between the two masses Solved Examples Example 1 Calculate the gravitational force if the mass of the sun is 199 × 10 30 kg and earth is 597 × 10 24 kg separated by the distance 15 × 10 11 m?(Gravitational constant




A Force Opposing Gravity Physics Stack Exchange




Chapter 2 Assess Your Progress Flashcards Quizlet
Terms in this set (39) What is inertial force an object's resistance to change in a state of rest or motion What is the appropriate force that occurs when the body accelerated foot ward The inertial forceA force of attraction between objects due to their mass Click again to see term 👆 Tap again to see term 👆 free fall Click card to see definition 👆 Tap card to see definition 👆 gravity is pulling down on an object and no other forces are acting on the object Click again to see term 👆1/04/17 · Gravity is the gravitational force that occurs between the earth and other bodies Gravity is the force acting to pull objects toward the earth Since gravitational force is happening to all matter (objects) in the universe, from the largest galaxies down to the smallest atoms, it is often called universal gravitation



Gravitational Force Quiz Flashcards Quizlet




Chap 13 All Flashcards Quizlet
According to Newton's universal law of gravitation, The force of attraction between any two bodies is directly proportional to the product of their masses andGravitational force definition, a unit of acceleration equal to the acceleration of gravity at the earth's surface Fighter pilots train to tolerate very high Gforces with breathing techniques and specialized equipment See moreGravitational Force Formula The gravitational force formula is also known as Newton's law of gravitation Also, it defines the magnitude of the force between two objects Furthermore, the gravitation force formula includes the gravitational constant whose value is G = 667 \(\times 10^{11} N \cdot m^{2}/ kg^ {2}\)




Physics 1 Chapter 4 Forces And Laws Of Motion Flashcards Quizlet




Astronomy 2 Flashcards Quizlet
· Gravitational force definition Newton's law of universal gravitation states that everybody of nonzero mass attracts every other object in the universe This attractive force is called gravityThe gravitational force which a planet or other body exerts upon its own material substance, atmosphere, etc, as opposed to that exerted by an external body In later use also the collective gravitational forces acting among the components of a body or massThe gravity of Earth, denoted by g, is the net acceleration that is imparted to objects due to the combined effect of gravitation and the centrifugal force In SI units this acceleration is measured in metres per second squared or equivalently in newtons per kilogram Near Earth's surface, gravitational acceleration is approximately 981 m/s2, which means that, ignoring the effects of




Space Technology Universal Expansion Gravitational Force Tides And Orbits Test Diagram Quizlet




7 2 Gravitational Fields Flashcards Quizlet
Use gravity to explain the relationship between Earth's orbit around the Sun ANSWER Although the Sun is very far way, its size keeps Earth in its orbit because of the gravitational force between the two masses Explain how resistance keeps two objects of the same weight from reaching the ground at the same time ANSWERGRAVITY, FORCE and WORK introduces Zog to Newton's basic laws of motion By observing objects on earth and in space, Zog learns that nothing can start moving3 Force and Gravity Being in orbit is like being infatuated – you are constantly falling, but you aren't getting closer The Force of Gravity Any two objects that have mass attract each other with a force we call gravity You probably never noticed this for small objects, because the force is so weak But the Earth




Physical Science Lesson 3 And Quiz 3 Flashcards Quizlet




Comparing Electric Force And Gravitational Force Practice Khan Academy
Forces of Attraction Gravity or gravitational forces are forces of attraction We're not talking about finding someone really cute and adorable It's like the Earth pulling on you and keeping you on the ground That pull is gravity at work Every object in the universe that has mass exerts a gravitational pull, or force, on every other · 2 Gravitational Force of the Sun The Sun has a gravitational force due to its mass, which is so large that its influence extends vastly All planets revolve around the Sun in elliptical orbits due to this attractive force The gravitational force between the Sun and Earth can be calculated using equation (1) Mass of the Sun M s = x 10 30 kg · G = 6673×10 11 N m 2 kg 2 It is typically used in the equation F = (G x m 1 x m 2) / r 2 , wherein F = force of gravity G = gravitational constant m 1 = mass of the first object (lets




Forces Gravity Friction Newton S Laws Diagram Quizlet




Lesson 7 Gravitational And Magnetic Fields Flashcards Quizlet




Centripetal Force Definition Quizlet




Ch 04 Astronomy Flashcards Quizlet




Ib Physics Topic 6 Gravitational Fields Forces Flashcards Quizlet




Gravity And Force Diagram Quizlet




Force And Motion Flashcards Quizlet




Science 8 Dc Identifying Forces Flashcards Quizlet




Ch 2 Work And Energy Diagram Quizlet




Universal Gravity Flashcards Quizlet




Astronomy Chapter 1 Earth Moon And Sun Diagram Quizlet




Gravitational Force Flashcards Quizlet




Csi Physical Science Unit 4 Matter In Motion Chapter 1 1 3 Forces And Motion Flashcards Quizlet




Ap Physics 1 Forces Calculated Flashcards Quizlet




Core 3 Properties Of Matter Vocab Flashcards Quizlet




Centrifugation Basics




Why Doesn T The Moon Crash Into The Earth Wired




Science Benchmark 3 Flashcards Quizlet




Barron S Ap Physics C Chapter 10 Universal Gravitation Diagram Quizlet




Test 2 Chapter 6 Uniform Circular Motion And Gravitation Flashcards Quizlet




Chap 13 All Flashcards Quizlet




Physics 2113 Final Flashcards Quizlet




Unit 7 Physics Relationship Between Force Motion And Energy Flashcards Quizlet




Vocabulary Universal Gravitation Flashcards Quizlet



2




Test 3 Chapter 12 Flashcards Quizlet




Gravitational Force Definition Quizlet




Centripetal Force Definition Quizlet




Astronomy 2 Flashcards Quizlet




Chapter 4 Test Diagram Quizlet




Gravity Key Ideas Flashcards Quizlet




Chap 13 All Flashcards Quizlet




Sph3u Unit 2 Gravitational Force Near The Earth Ppt Download




Physical Science Lesson 3 And Quiz 3 Flashcards Quizlet




Mastering Physics Set 1 Midterm 1 Flashcards Quizlet




Gravity And Motion Flashcards Quizlet




Centripetal Force Definition Quizlet




Mastering Physics Set 1 Midterm 1 Flashcards Quizlet




Physics A Level Gravitational Fields Flashcards Quizlet




Physics Final Exam Chapter 5 4 3 2 1 Flashcards Quizlet




Motion And Forces Chapter 2 Reading Study Guide A Answers




Gravity Flashcards Quizlet




Mastering Physics Set 1 Midterm 1 Flashcards Quizlet




Newton S Laws Of Gravity Diagram Quizlet




P2 Matter And Forces Flashcards Quizlet




Chapter 13 Satellite And Projectile Motion Flashcards Quizlet




Ib Physics Topic 6 Gravitational Fields Forces Flashcards Quizlet




Gravitational Force Flashcards Quizlet




Gravitational Force Flashcards Quizlet




Forces Flashcards Quizlet




Mcat Physics Flashcards Quizlet



Curious Kids Why Is The Earth Round




Forces Mass And Weight Flashcards Quizlet




Ib Physics Topic 6 2 And 10 2 Gravitation Diagram Quizlet




Gravity Key Ideas Flashcards Quizlet




Science Chap13 Interactive Reader Flashcards Quizlet




Chapter 7 Circular Motion Flashcards Quizlet




Unit 3 The Solar System Flashcards Quizlet




Abeka Grade 9 Science Test 7 Flashcards Quizlet




Chapter 2 Force Flashcards Quizlet




Chapter 10 Section 2 Flashcards Quizlet




Exam 1 Study Guide Flashcards Quizlet




Gravitational Force Definition Quizlet




Circular Motion And Gravitation Sl Flashcards Quizlet




Gravity Flashcards Quizlet




Force And Motion Flashcards Quizlet




Unit 4 Physics Review Flashcards Quizlet




Force And Motion Flashcards Quizlet




Slope Processes Development Lesson 8




Universal Gravity Flashcards Quizlet




Conceptual Physical Science Final Exam Chapter 4 Gravity Diagram Quizlet




Solar System Flashcards Quizlet




Gravity And Orbit 42 Flashcards Quizlet




Sph3u Unit 2 Gravitational Force Near The Earth Ppt Download




Circular Motion And Gravitation Sl Flashcards Quizlet




Gravity Key Ideas Flashcards Quizlet




Astronomy Test 3 Flashcards Quizlet
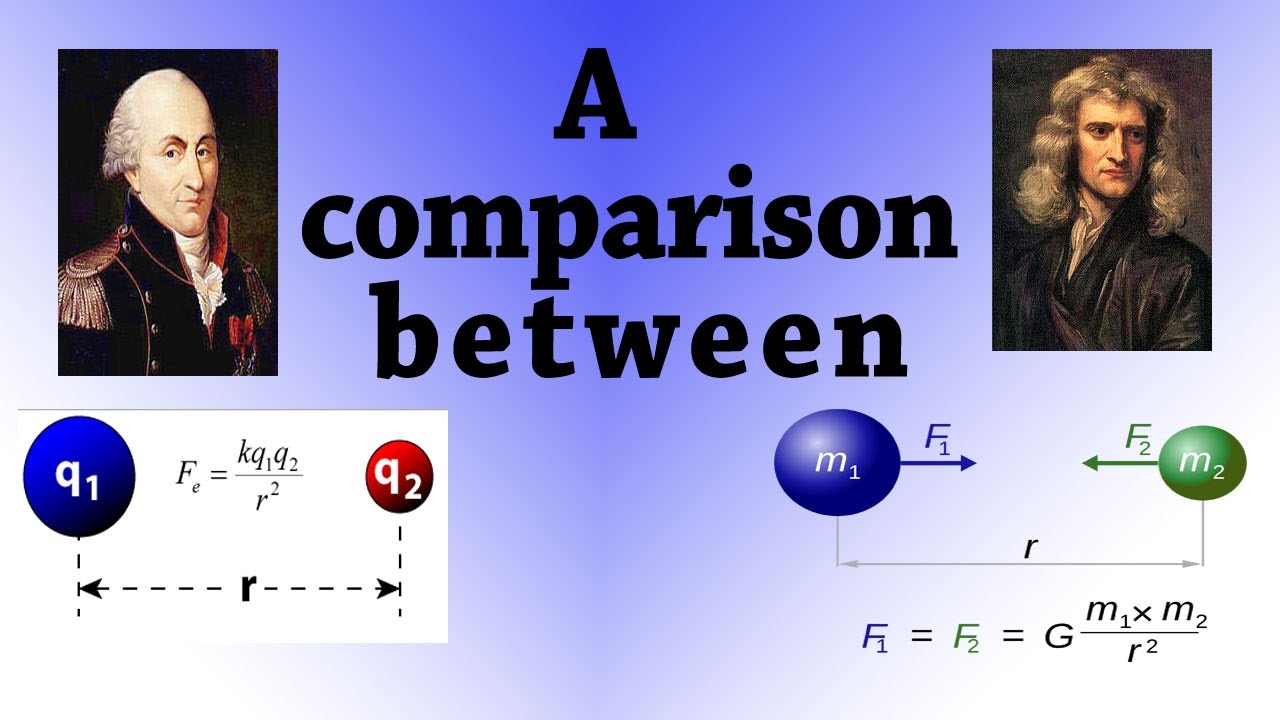



Difference Between Gravitational Force And Electrostatic Force Physicsabout


コメント
コメントを投稿